Heater Modules for High-Temperature Applications
Our heater modules offer a cost-effective, high-performance solution using market-leading heater technology. Designed for use in a range of applications, from ultra-high vacuum (UHV) environments to high-temperature processes, these modules are an excellent choice for integrating into custom heater stage designs or as standalone components.
Key Features
- High Uniformity Heating: Achieves high uniformity heating up to 1200°C, crucial for precise thermal control and optimal performance in demanding applications.
- Efficient Radiating Surface: Features elements with a large radiating surface to gap ratio, enabling operation at lower temperatures compared to conventional metal heaters, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Refractory Metal Construction: The refractory metal hot zone, made from materials like Molybdenum and Tantalum, ensures uncompromised performance even at extreme temperatures, making these modules ideal for high-temperature environments.
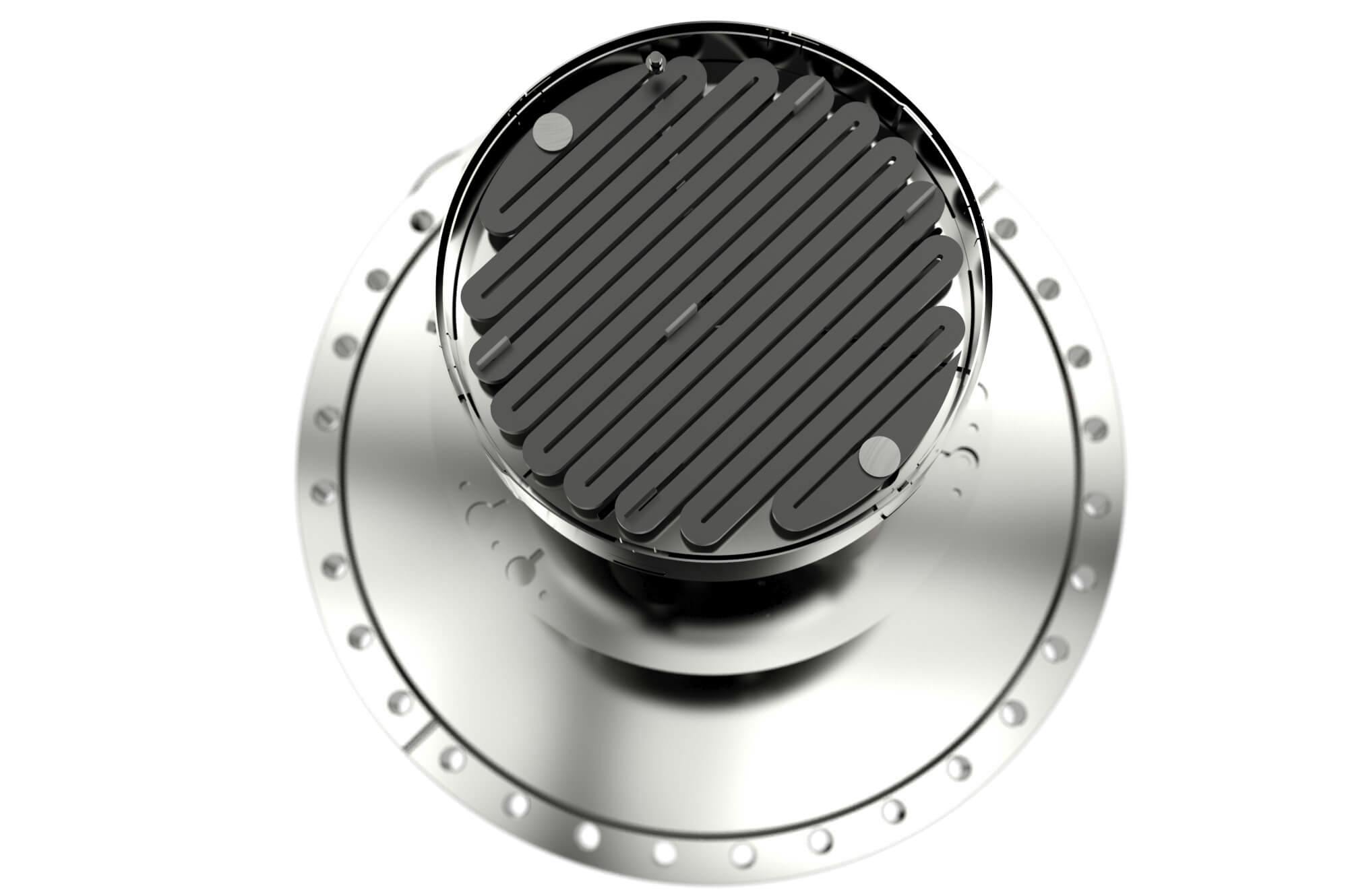

Heater Module Overview
Our heater modules are equipped with CVD processed heating elements, housed in durable refractory metal cases. They are designed for versatility and can be used in:
- Vacuum applications for radiant heating of semiconductor wafers and other substrates.
- Holder-supported samples and various other materials requiring high-temperature treatment.
The immediate hot zone, constructed from refractory metals and ceramics, is free from materials that could degrade performance at high temperatures, making these modules particularly suitable for ultra-high vacuum (UHV) and high-pressure applications.
Choosing the right element
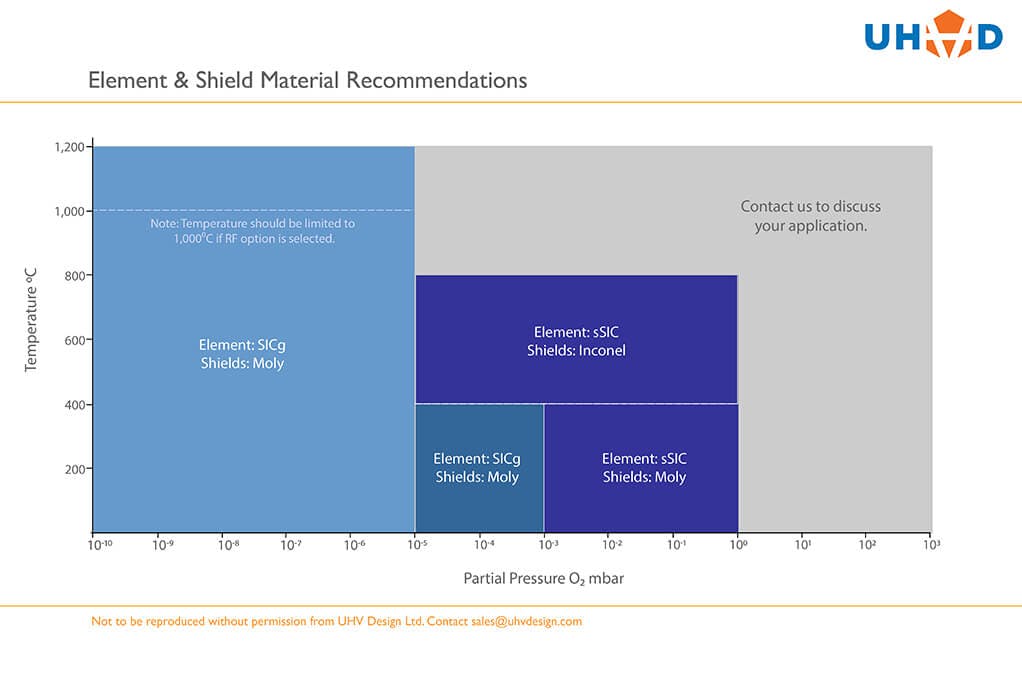
SiCg Elements: Silicon Carbide-coated Graphite (SiCg) elements provide enhanced durability in oxidising atmospheres compared to traditional graphite. They are ideal for applications involving high partial pressures of oxygen.
sSiC Elements: Solid Silicon Carbide (sSiC) elements are manufactured from conducting solid SiC material in the ß phase, offering superior robustness, oxidation resistance, and temperature uniformity. With a large radiating surface to gap ratio, sSiC elements run at lower temperatures than metal wire heaters, ensuring excellent substrate heating uniformity and extended heater longevity.
Our heater modules are designed to meet the demanding requirements of high-performance applications, providing reliable and efficient heating solutions for a wide range of industrial and research needs.
Product configuration tool
If you would like to discuss your project with our engineering team, please contact us.